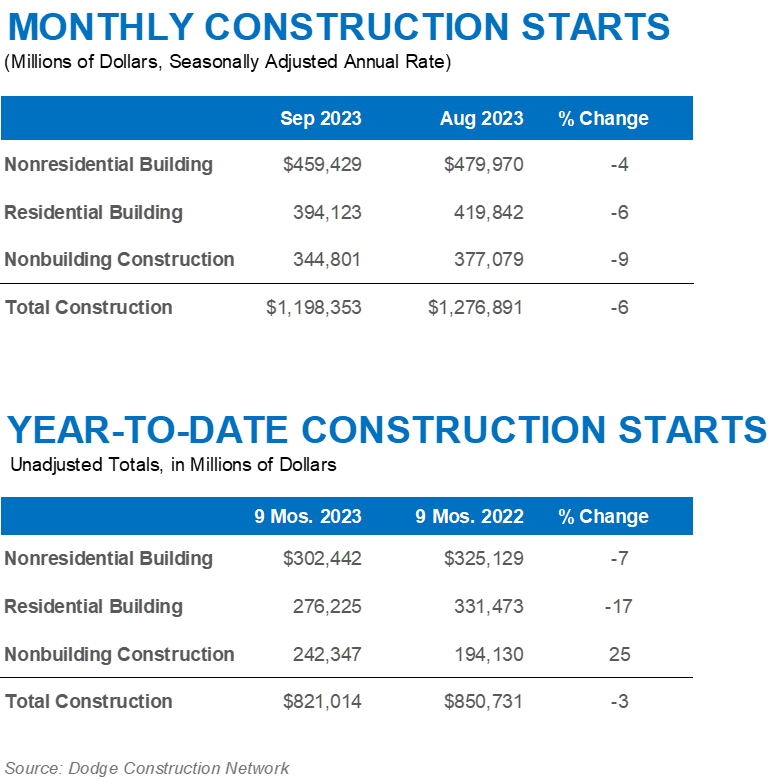
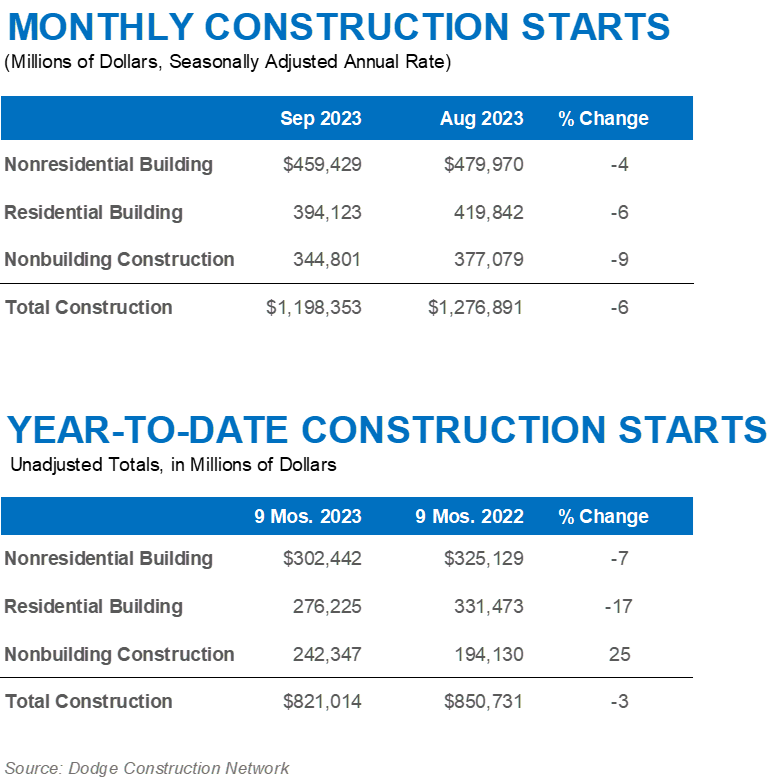
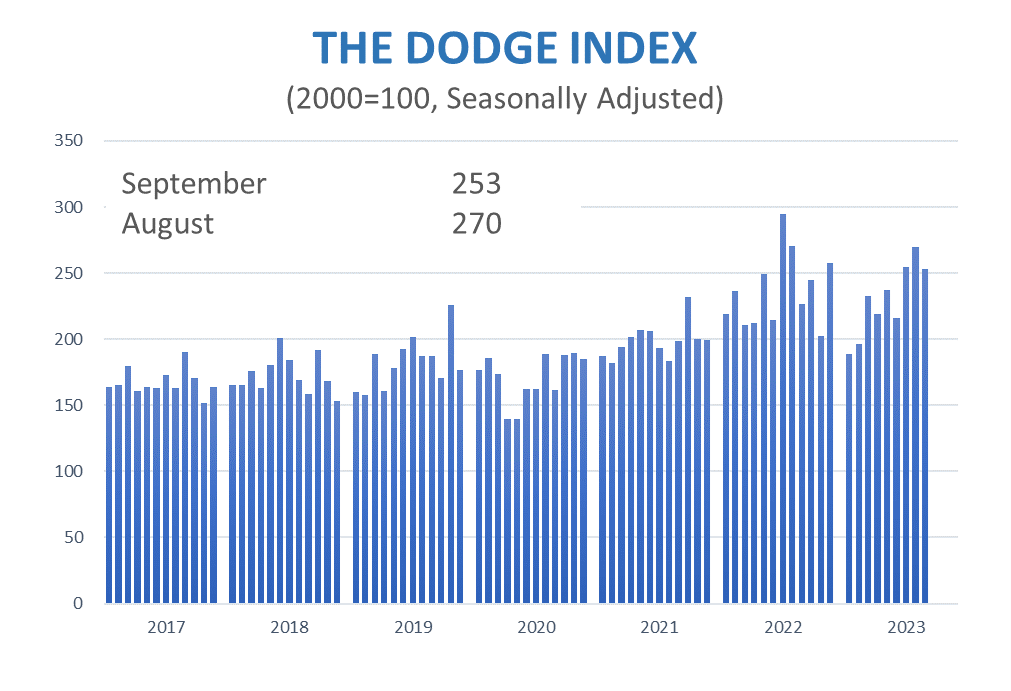
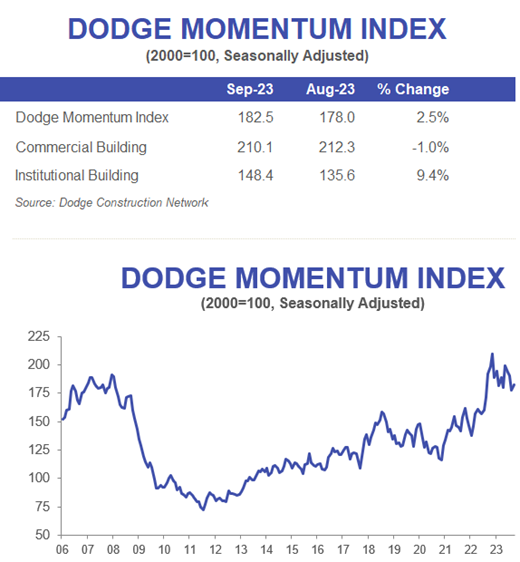
The latest safety management study reveals an increase in the implementation of safety and health strategies, but those measures could have greater adoption across the industry.
HAMILTON, NJ – October 26, 2023 – Research findings released today indicate construction contractors continue to make progress responding to issues affecting worker safety and health, such as heat and mental health, but many areas for improvement remain.
The new study, Safety Management in the Construction Industry 2023 SmartMarket Report, examines occupational safety and health challenges across the industry and shines a light where more effort is needed. It was conducted by Dodge Construction Network (DCN), the industry-leading source of construction data and insight, and CPWR, a nonprofit dedicated to reducing occupational injuries, illnesses and fatalities in construction.
HEAT
Working in extreme heat is increasingly common in construction, posing significant safety and health risks to workers. To combat this problem:
- 52% of contractors in the study report making changes at their company in the last three years to prevent heat-related illnesses onsite.
- 66% of contractors implemented a heat-safety policy at their company.
The most common practices to address heat-related issues are providing water, rest and shade and worker training. Less common practices are monitoring the environment for heat hazards and administrative controls such as pausing work in the hottest parts of the day.
But while the data indicate progress, there are large disparities by company size. Only 21% of employers with less than 20 employees made changes to address heat in the last three years, and another 21% of the small contractors do not consider heat stress an issue at all.
“Employers need to provide workplaces that control recognized hazards, including heat,” said Chris Trahan Cain, CPWR’s executive director. “Many firms are showing that protecting their workers from excessive heat is good for safety and good for business, but this report shows many still are not.”
MENTAL HEALTH, SUICIDE, AND OPIOID USE
When asked about topics about which they want additional training and information, such as through webinars, factsheets, infographics, and toolbox talks, the study revealed a high level of interest on worker wellbeing. Fifty-two percent of contractors wanted more resources for managing mental health, suicide, and opioid use.
The next most frequently cited topic was lifting or ergonomics, safety at 34%. This is a striking finding considering that the rest of the list consists of well-known hazards that still plague the industry.
Contractors were asked whether their company provides a program for substance use or mental health, such as access to professional services. There were major differences depending on company size:
- 80% of large contractors (100 or more employees) offer programs for substance use or mental health.
- Only 29% of small companies (fewer than 20 employees) offer these programs.
Strategies like having a peer network to address substance use or mental health are relatively uncommon, but more frequent among large contractors and those that employ union craftworkers.
PRE-PROJECT AND PRE-TASK ENGAGEMENT
The study also examines the use and subsequent advantages of other good safety practices on the jobsite, including during pre-construction and pre-task planning. Both strategies show the clear benefits of engaging multiple viewpoints in these processes:
- 94% of contractors who engaged in most (7 or more) of these activities reported an increase in worker engagement with safety measures.
- 84% of those contractors reported a reduction in recordable injury rates.
- 60% of those contractors saw an improvement in productivity.
The study also examined other good safety practices, including the use of right-sized PPE, online training, and the use of technology. It found that one of the biggest opportunities for contractors to improve safety is to use data gathered on their projects more effectively: nearly one-quarter of the contractors who collect project safety data said they do not analyze it.
IMPLEMENTATION ACROSS COMPANIES
The study also dives into the effective implementation of safety practices among firms of different sizes, as well as ways to improve. For example, the study highlights safety measures that smaller firms could use that larger firms have already adopted. These methods include getting workers more engaged in pre-task planning and using free online tools to promote worker well-being.
“Many small companies don’t have dedicated safety managers like you would see at a larger company, so data like this is particularly valuable to help provide education about how the industry is improving worker safety, health and well-being,” says Donna Laquidara-Carr, industry insights research director at Dodge Construction Network.
Since 2012, DCN and CPWR have partnered to deliver studies on construction safety management. Previous reports examined commonly used safety practices and the corresponding benefits contractors experience from investments in safety. The Safety Management in the Construction Industry 2023 SmartMarket Report contains more detailed findings and analysis on each of these topics including feature articles and case studies illuminating how these insights can be more widely implemented across the industry. The report can be downloaded here.
About CPWR: CPWR – The Center for Construction Research and Training is a 501(c)(3) not-for-profit created by North America’s Building Trades Unions (NABTU). Its mission is to reduce occupational injuries, illnesses and fatalities in the construction industry through research, training, and service programs. CPWR is uniquely situated to serve U.S. construction workers, contractors and the research community, having partnered with the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) in NIOSH’s construction safety and health research initiative for three decades.
The post Contractors Are Addressing Safety and Health Issues, But They Can Do More appeared first on Dodge Construction Network.
Source: New feed